This page was last updated: April 16, 2019
For each original Cartesian coordinate pair (x,y):
int Npts[68];
float X[68][263];
float Y[68][263];
<< in InitGraphics( ): >>
FILE *fp = fopen( "proj04.dat", "r" );
if( fp == NULL )
{
fprintf( stderr, "Cannot open 'proj07.dat' !\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
for( int i = 0; i < 68; i++ )
{
fscanf( fp, "%d", &Npts[i] );
for( int j = 0; j < Npts[i]; j++ )
{
fscanf( fp, "%f %f", &X[i][j], &Y[i][j] );
}
}
fclose( fp );
<< In Display( ): >>
for( int i = 0; i < 68; i++ )
{
glBegin( GL_LINE_STRIP );
for( int j = 0; j < Npts[i]; j++ )
{
?????
glVertex2f( ??, ?? );
}
glEnd( );
}
struct xy
{
float x, y;
};
int Npts[68];
struct xy *Outlines[68];
<< in InitGraphics( ): >>
FILE *fp = fopen( "proj04.dat", "r" );
if( fp == NULL )
{
fprintf( stderr, "Cannot open 'proj07.dat' !\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
for( int i = 0; i < 68; i++ )
{
fscanf( fp, "%d", &Npts[i] );
Outlines[i] = (struct xy *) malloc( Npts[i] * sizeof(struct xy) );
for( int j = 0; j < Npts[i]; j++ )
{
fscanf( fp, "%f %f", &Outlines[i][j].x, &Outlines[i][j].y );
}
}
<< In Display( ): >>
for( int i = 0; i < 68; i++ )
{
glBegin( GL_LINE_STRIP );
for( int j = 0; j < Npts[i]; j++ )
{
?????
glVertex2f( ??, ?? );
}
glEnd( );
}
struct xy
{
float x, y;
};
class Linestrip
{
public:
int npts; // # of points in the line strip
struct xy *pts; // array of point structures
// constructor:
Linestrip( int n = 100 )
{
npts = n;
pts = new struct xy[n];
}
// method to display the linestrip:
void
Display( )
{
glBegin( GL_LINE_STRIP );
for( int i = 0; i < npts; i++ )
{
?????
glVertex2f( ??, ?? );
}
glEnd( );
}
};
. . .
Linestrip *Outlines[68]; // 68 linestrips in usa map
. . .
<< In InitGraphics( ): >>
FILE *fp = fopen( "proj04.dat", "r" );
if( fp == NULL )
{
fprintf( stderr, "Cannot open 'proj07.dat' !\n" );
exit( 1 );
}
for( int i = 0; i < 68; i++ )
{
fscanf( fp, "%d", &npts );
Outlines[i] = new Linestrip( npts );
for( int j = 0; j < npts; j++ )
{
fscanf( fp, "%f %f", &Outlines[i]->pts[j].x, &Outlines[i]->pts[j].y );
}
}
<< In Display( ): >>
for( int i = 0; i < 68; i++ )
{
Outlines[i]->Display( );
}
As this is a pure 2D application:
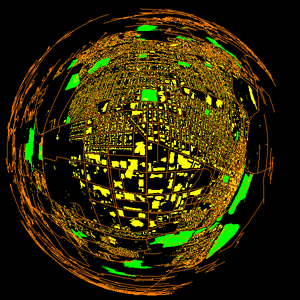
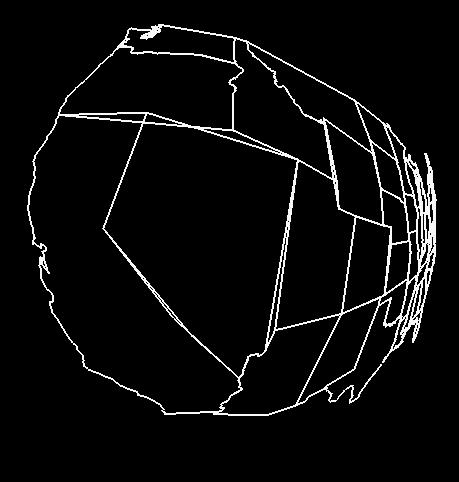
Because hyperbolic geometry uses a nonlinear equation, but we are drawing long lines, you get display cracks where there are T-intersections in the model, like this:
Break each line segment into many line segments so that long straight lines appear curved as shown here:
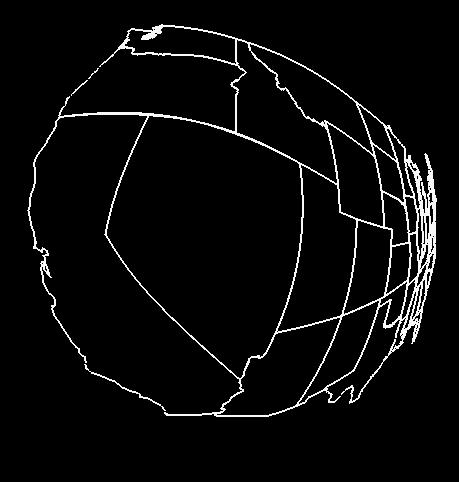
x = (1.-t) * x0 + t * x1 y = (1.-t) * y0 + t * y1 0. <= t <= 1.
| Item | Points |
| Draw a USA-looking map | 10 |
| Draw a correct Polar USA map | 20 |
| Draw a correct Cartesian USA map | 20 |
| Translation | 10 |
| Change K with a GLUI spinner or slider | 20 |
| Extra Credit | 5 |
| Potential Total | 85 |